Page 962 - MiSUMi FA Mechanical Components Economy Series
P. 962
[Technical Data]
SI (International System of Units) Excerpted from GB 3100—1993
1. International System of Units(SI)and Usage.
1-1. Scope of Application This standard specifies how to use the International System of Units(SI) and other international unitary systems, as well as
units used in correlation with units from international systems, and other units which may be used.
1-2. Terms and Defi nitions Terminology used in this specification and definitions thereof are as follows.
(1) International System of Units(SI) Coherent system of units adopted and recommended by the International Committee on Weights and Measures.
It contains base units and supplementary units, units derived from them and their integral exponents to the 10th power.
(2) SI Unit Generic term used to describe base units, supplementary units or derived units of the International System of Units(SI).
(3) Base Unit Those units are given in Table 1.
(4) Supplementary Units Those supplementary units are given in Table 2.
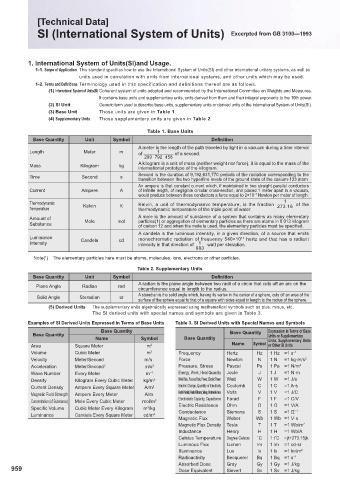
Table 1. Base Units
Base Quantity Unit Symbol Defi nition
A meter is the length of the path traveled by light in a vacuum during a time interval
1
Length Meter m of of a second.
299 792 458
A kilogram is a unit of mass (neither weight nor force), it is equal to the mass of the
Mass Kilogram kg
international prototype of the kilogram.
Second is the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the
Time Second s
transition between the two hyperfi ne levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom
An ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors
Current Ampere A of infi nite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1 meter apart in a vacuum,
would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2×10 Newton per meter of length.
−7
1
Thermodynamic Kelvin K Kelvin, a unit of thermodynamic temperature, is the fraction of the
Temperature thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water. 273.16
Amount of A mole is the amount of substance of a system that contains as many elementary
Substance Mole mol particles(1) or aggregation of elementary particles as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram
of carbon 12 and when the mole is used, the elementary particles must be specifi ed.
A candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits
Luminance monochromatic radiation of frequency 540×10 hertz and that has a radiant
12
Intensity Candela cd intensity in that direction of watt per steradian.
1
683
Note( ) The elementary particles here must be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons or other particles.
1
Table 2. Supplementary Units
Base Quantity Unit Symbol Defi nition
A radian is the plane angle between two radii of a circle that cuts off an arc on the
Plane Angle Radian rad
circumference equal in length to the radius.
A steradian is the solid angle which, having its vertex in the center of a sphere, cuts off an area of the
Solid Angle Steradian sr
surface of the sphere equal to that of a square with sides equal in length to the radius of the sphere.
(5) Derived Units The supplementary units algebraically expressed using mathematical symbols such as plus, minus, etc.
The SI derived units with special names and symbols are given in Table 3.
Examples of SI Derived Units Expressed in Terms of Base Units Table 3. SI Derived Units with Special Names and Symbols
Base Quantity Base Quantity Expression in Terms of Base
Base Quantity Units or Supplementary
Name Symbol Base Quantity Units, Supplementary Units
Area Square Meter m 2 Name Symbol or Other SI Units
Volume Cubic Meter m 3 Frequency Hertz Hz 1 Hz =1 s −1
Velocity Meter/Second m/s Force Newton N 1 N =1 kg·m/s 2
Acceleration Meter/Second 2 m/s 2 Pressure, Stress Pascal Pa 1 Pa =1 N/m 2
Wave Number Every Meter m −1 Energy, Work, Heat Quantity Joule J 1 J =1 N·m
Density Kilogram Every Cubic Meter kg/m 3 Work Rate, Process Rate, Power, Electric Power Watt W 1 W =1 J/s
Current Density Ampere Every Square Meter A/m 2 Electric Charge, Quantity of Electricity Coulomb C 1 C =1 A·s
Magnetic Field Strength Ampere Every Meter A/m Electric Potential, Potential Diff erence, Voltage, Electromotive Force Volts V 1 V =1 J/C
Concentration (of Substance) Mole Every Cubic Meter mol/m 3 Electrostatic Capacity, Capacitance Farad F 1 F =1 C/V
Specifi c Volume Cubic Meter Every Kilogram m /kg Electric Resistance Ohm Ω 1 Ω =1 V/A
3
−1
Luminance Candela Every Square Meter cd/m 2 Conductance Siemens S 1 S =1 Ω
Magnetic Flux Weber Wb 1 Wb =1 V·s
Magnetic Flux Density Tesla T 1 T =1 Wb/m 2
Inductance Henry H 1 H =1 Wb/A
Celsius Temperature Degree Celsius ˚C 1 t˚C =(t+273.15)k
Luminous Flux Lumen lm 1 lm =1 cd·sr
Illuminance Lux lx 1 lx =1 lm/m 2
Radioactivity Becquerel Bq 1 Bq =1 s −1
Absorbed Dose Gray Gy 1 Gy =1 J/kg
959 Dose Equivalent Sievert Sv 1 Sv =1 J/kg