Page 982 - MiSUMi FA Mechanical Components Economy Series
P. 982
[Materials]
Hardening and Hardness Test Methods
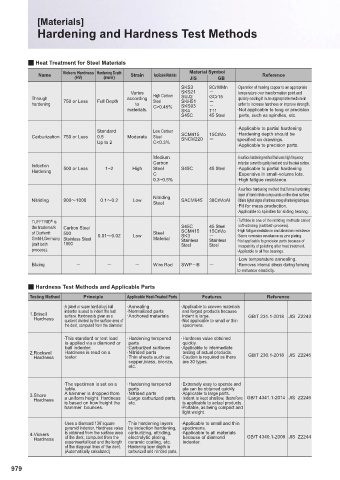
Q Heat Treatment for Steel Materials
Name Vickers Hardness Hardening Depth Strain Applicable Materials Material Symbol Reference
(HV)
(mm)
GB
JIS
SKS3 9CrWMn · Operation of heating copper to an appropriate
Varies SKS21 temperature over transformation point and
Through Full Depth according High Carbon SUJ2 GCr15 quickly cooling it in an appropriate medium in
Steel
hardening 750 or Less to C>0.45% SKH51 order to increase hardness or improve strength.
SKS93
materials. SK4 T11 · Not applicable to long or precision
S45C 45 Steel parts, such as spindles, etc.
·Applicable to partial hardening
Standard Low Carbon
Carburization 750 or Less 0.5 Moderate Steel SCM415 15CrMo ·Hardening depth should be
SNCM220
Up to 2 C<0.3% specifi ed on drawings.
·Applicable to precision parts.
Medium · A surface hardening method that uses high frequency
Carbon induction current to quickly heat and cool the steel surface.
Induction
Hardening 500 or Less 1~2 High Steel S45C 45 Steel ·Applicable to partial hardening
C ·Expensive in small-volume lots.
0.3~0.5% ·High fatigue resistance.
· A surface hardening method that forms hardening
layer of hard nitride compounds on the steel surface
Nitriding
Nitriding 900։1000 0.1։0.2 Low SACM645 38CrMoAl ·Obtains highest degree of hardness among all hardening techniques.
Steel
·Fit for mass production.
·Applicable to spindles for sliding bearing.
TUFFTRID is · Tuff tride is one of the nitriding methods called
®
the trademark Carbon Steel S45C 45 Steel soft-nitriding (salt bath process).
of Durferrit 500 Steel SCM415 15CrMo · High fatigue resistance and abrasion resistance
· Same corrosion resistance as zinc plating.
GmbH‚Germany Stainless Steel 0.01։0.02 Low Material SK3 · Not applicable to precision parts because of
Stainless
Stainless
(salt bath 1000 Steel Steel incapability of polishing after heat treatment.
process). ·Applicable to oil free bearings.
·Low temperature annealing.
Bluing Wire Rod SWPB ·Removes internal stress during forming
to enhance elasticity.
Q Hardness Test Methods and Applicable Parts
Testing Method Principle Applicable Heat-Treated Parts Features Reference
· A (steel or super hard alloy) ball ·Annealing · Applicable to uneven materials
indenter is used to indent the test ·Normalized parts and forged products because
1. Brinell surface. Hardness is given as a ·Anchored materials indent is large. GB/T 231.1-2018 JIS Z2243
Hardness quotient divided by the surface area of · Not applicable to small or thin
the dent, computed from the diameter. specimens.
· This standard or test load · Hardening tempered · Hardness value obtained
is applied via a diamond or parts quickly.
ball indenter. ·Carburized surfaces · Applicable to intermediate
2. Rockwell Hardness is read on a ·Nitrided parts testing of actual products.
Hardness tester. · Thin sheets such as · Caution is required as there GB/T 230.1-2018 JIS Z2245
copper,brass, bronze, are 30 types.
etc.
· The specimen is set on a · Hardening tempered · Extremely easy to operate and
table. parts ata can be obtained quickly.
3. Shore A hammer is dropped from ·Nitrided parts ·Applicable to large parts.
Hardness a uniform height. Hardness · Large carburized parts, · Indent is kept shallow, therefore GB/T 4341.1-2014 JIS Z2246
is based on how height the etc. is applicable to actual products.
hammer bounces. · Portable, as being compact and
light weight.
· Uses a diamond 136˚square · This hardening layers · Applicable to small and thin
pyramid indenter. Hardness value by induction hardening, specimens.
4. Vickers is obtained from the surface area carburizing, nitriding, · Applicable to all materials
Hardness of the dent, computed from the electrolytic plating, because of diamond GB/T 4340.1-2009 JIS Z2244
experimental load and the length ceramic coating, etc. indenter.
of the diagonal lines of the dent. · Hardening layer depth in
(Automatically calculated) carburized and nitrided parts.
979