Page 61 - CETA WORLD HIGH SCHOOL GUIDE 2022
P. 61
4<Y':'%&a4,:+*"',&Y':'%[
A-level is the two final years of schooling according to the British Cur- the A-level test. All of this was done to modify teaching content of the the two-year
riculum. A-level curriculum allows students to enroll only in the subjects of their curriculum to be more intensive and appropriate for further studying in a university level
interests, instead of enrolling every compulsory subject. Hence students can choose Both GCSEs and A-level have undergone a curriculum reform. In September,
only the subjects that they are interested in or good at. However, there has to be some 2015 the first group of subjects were modified, and the examination of this revised
relevance between the selected subjects and the intended courses at the university curriculum was first held in 2017. The reform stages varied across subject groups. Both
level. There are more than 50 subjects in the A-level curriculum covering academic GCSEs and A-levels were reformed, transitioning from a modular to linear structure.
knowledge, languages, arts, music as well as sports. There is a combination of theories Students are required to sit for an examination in the final semester of the second
and practical knowledge, providing students with skills and experience in order to be year. Regarding AS-level, it is now a separate qualification and is not required for an
ready for university entrance based on their targeted field of study. A-Level award. The new curriculum increasingly emphasizes subjects like calculation
There are basically two rounds of A-levels assessment, however, in 2016 in mathematics, grammar, punctuation, pronunciation and Pre 20th Century Literature
the scoring of AS-Levels was terminated. Hence, scoring is now based on the last in English. Regarding A-level, students can choose 3-4 subjects according to their
round of A-level test or year 13. Students can then use scores from each subject to interest and aptitude. The teaching content in A-level is more intensive than that of
apply for university entrance. Anyway, AS-Level (Year 12) tests are still offered for GCSE. Students can further consult with schools’ counselors for curriculum selection.
students to assess themselves, but the score will not be taken into consideration with
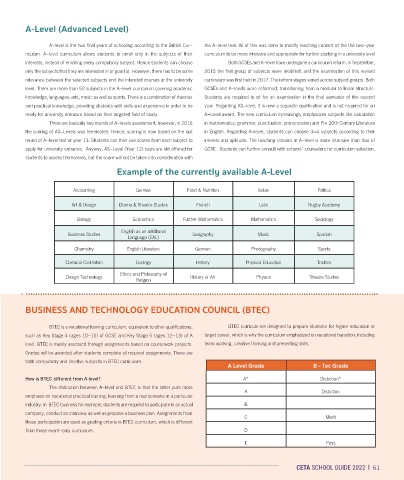
5I+;2%'&$G&(#'&".33'*(%=&+:+)%+>%'&4<Y':'%
Accounting German Food & Nutrition Italian Politics
Art & Design Drama & Theatre Studies French Latin Rugby Academy
Biology Economics Further Mathematics Mathematics Sociology
Business Studies English as an additional Geography Music Spanish
Language (EAL)
Chemistry English Literature German Photography Sports
Classical Civilization Geology History Physical Education Textiles
Design Technology Ethics and Philosophy of History of Art Physics Theatre Studies
Religion
@7!QZ5!!&4ZU&65-KZPYP9b&5U7-46QPZ&-P7Z-QY&a@65-[
BTEC is a vocational training curriculum, equivalent to other qualifications, BTEC curricula are designed to prepare students for higher education or
such as Key Stage 4 (ages 10-11) of GCSE and Key Stage 5 (ages 12-13) of A target career, which is why the curriculum emphasized on vocational transition, including
level. BTEC is mainly assessed through assignments based on coursework projects. team working, creative thinking and presenting skills.
Grades will be awarded after students complete all required assignments. There are
both compulsory and elective subjects in BTEC curriculum.
4&Y':'%&93+,' @&<&6'"&93+,'
H ow is BTEC different from A- lev el? A* Distiction*
The distinction between A-level and BTEC is that the latter puts more A Distiction
emphasis on vocational practical training, learning from a real scenario in a particular
industry. In BTEC business for example, students are required to participate in an actual B
company, conduct an interview as well as propose a business plan. Assignments from C Merit
these participation are used as grading criteria in BTEC curriculum, which is different
from those exam-only curriculum. D
E Pass
-'.*"$%&''(")*+,-"./..""#""P$