Page 13 - วิชาการพยาบาลสาธารณภัยเล่มที่ 2 : สถาบันการพยาบาลศรีสวรินทิรา สภากาชาดไทย
P. 13
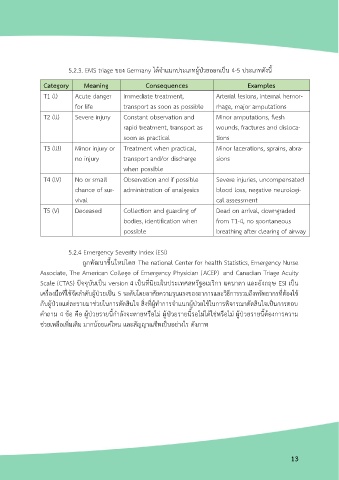
5.2.3. EMS triage ของ Germany ได้จ าแนกประเภทผู้ป่วยออกเป็น 4-5 ประเภทดังนี้
Category Meaning Consequences Examples
T1 (l) Acute danger Immediate treatment, Arterial lesions, internal hemor-
for life transport as soon as possible rhage, major amputations
T2 (ll) Severe injury Constant observation and Minor amputations, flesh
rapid treatment, transport as wounds, fractures and disloca-
soon as practical tions
T3 (lll) Minor injury or Treatment when practical, Minor lacerations, sprains, abra-
no injury transport and/or discharge sions
when possible
T4 (lV) No or small Observation and if possible Severe injuries, uncompensated
chance of sur- administration of analgesics blood loss, negative neurologi-
vival cal assessment
T5 (V) Deceased Collection and guarding of Dead on arrival, downgraded
bodies, identification when from T1-4, no spontaneous
possible breathing after clearing of airway
5.2.4 Emergency Severity Index (ESI)
ถูกพัฒนาขึ้นใหม่โดย The national Center for health Statistics, Emergency Nurse
Associate, The American College of Emergency Physician (ACEP) and Canadian Triage Acuity
Scale (CTAS) ปัจจุบันเป็น version 4 เป็นที่นิยมในประเทศสหรัฐอเมริกา แคนาดา และอังกฤษ ESI เป็น
เครื่องมือที่ใช้จัดล าดับผู้ป่วยเป็น 5 ระดับโดยอาศัยความรุนแรงของอาการและวิธีการรวมถึงทรัพยากรที่ต้องใช้
กับผู้ป่วยแต่ละรายมาช่วยในการตัดสินใจ สิ่งที่ผู้ท าการจ าแนกผู้ป่วยใช้ในการพิจารณาตัดสินใจเป็นการตอบ
ค าถาม 4 ข้อ คือ ผู้ป่วยรายนี้ก าลังจะตายหรือไม่ ผู้ป่วยรายนี้รอไม่ได้ใช่หรือไม่ ผู้ป่วยรายนี้ต้องการความ
ช่วยเหลือเพิ่มเติม มากน้อยแค่ไหน และสัญญาณชีพเป็นอย่างไร ดังภาพ
13